
SEEING THE LIGHT
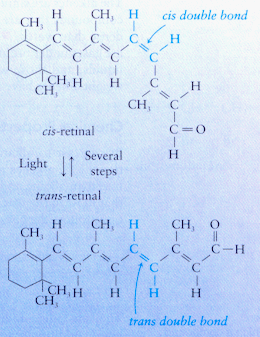
Cis-trans isomerism is important in several biological processes, one of which is vision. When light strikes the retina, a cis double bond in the cormpound retinal (structurally related to vitamin A) is converted to a trans double bond. The conversion triggers a chain of events that finally results in our being able to see.
In a series of steps, trans-retinal is enzymatically converted back to cis-retinal so that the cycle can be repeated. Bright light temporarily destroys our ability to see in dim light because large quantities of cis-retinal are rapidly converted to the trans isomer by the bright light. It takes time for conversion of the trans-retinal back to cis-retinal.
|
|
¡@